All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Upregulation of Antioxidant Gene Expressions and Enzyme Activity Against Acrylamide-Induced Neurotoxicity in Mice after Grape Seed Extract Treatment
Abstract
Background:
The risk of occupational exposure to acrylamide is high and long-term acrylamide exposure can cause neurotoxicity. Thus, therapeutic agents that can protect against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity are needed.
Objective:
To investigate whether Grape Seed Extract (GSE) protects against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in mice.
Methods:
Mice were divided into saline, GSE, acrylamide, GSE followed by acrylamide, acrylamide followed by GSE, and simultaneous acrylamide and GSE treatment groups. Gene expression and antioxidant enzyme levels were then determined using RT-PCR and biochemical assays.
Results:
Gpx1 (P < 0.05), Prdx3 (P < 0.01), SOD1 (P < 0.05), and CAT (P < 0.05) significantly upregulated in GSE-treated mice, compared to those in untreated controls. In contrast, Gpx1 (P < 0.05), Prdx3 (P < 0.05), SOD1 (P < 0.05), and CAT (P < 0.05) significantly downregulated in acrylamide-treated mice compared to those in untreated controls. Results of the treatment with GSE before exposure to acrylamide or simultaneously with acrylamide indicated that GSE restored Gpx1, Prdx3, SOD1, and CAT expression to similar levels as those in the control group. GSE treatment after exposure to acrylamide did not exert any neuroprotective effects against acrylamide, as revealed by significant downregulation of Gpx1 (P < 0.05), Prdx3 (P < 0.01), SOD1 (P < 0.05), and CAT (P < 0.05) compared to that in untreated controls. Animals treated with grape seed before acrylamide treatment showed no significant change in LPO activities and a significant increase in GSH levels, compared to those in untreated controls.
Conclusion:
GSE exerted neuroprotective effects against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity. Acrylamide caused oxidative stress 20 days post-exposure. However, grape seed treatment before exposure to acrylamide restored all test parameters to levels similar to control values.
1. INTRODUCTION
Acrylamide (C3H5NO), also known as prop-2-enamide or acrylic amide, has a relative molecular mass of 71.08 Da [1-4]. Acrylamide can act as an effective neurotoxin (nerve toxin) in humans and animals [5-7]. Moreover, its polymer, polyacrylamide, can be used in a range of industrial processes, such as food processing, water treatment, as well as for paper, petroleum, agriculture, cosmetics, and medicine manufacture [8, 9]. Such high utility indicates a high risk of occupational contact or exposure to acrylamide as a pollutant [10]. In areas where polyacrylamides are used in industries, acrylamide is detected in the drinking-water. This can unknowingly lead to oral ingestion of acrylamide [11]. Acrylamide is quickly absorbed and distributed/spread among the animals, as has been observed through examinations carried out after oral administration of acrylamide to animals in previous studies [11]. Management of water pollution, either by cleaning-up and/or attenuation of acrylamide in the polluted water, is an effective way to avoid such pollution.
Long-term acrylamide exposure can cause neurotoxicity, which is characterized by skeletal muscle weakness, ataxia, numbness of the hands and feet, gait abnormalities, and cognitive deficits [12]. Toxicological studies imply that acrylamide vapors can irritate the skin and eyes and cause paralysis of the cerebrospinal system [13-15]. Studies conducted with laboratory animals, including guinea pigs, rodents, rabbits, dogs, and cats, have indicated that daily exposure to acrylamide (0.5–50 mg/kg per day) causes neurological changes similar to those observed during neurotoxicity in humans [16].
Within cells, acrylamide is metabolized to glycidamide (C3H5NO2), which may be the metabolite responsible for the genotoxic effects of acrylamide [17]. Glycidamide can form DNA adducts in animal and human tissues, both in vivo and in vitro. In fact, many studies have used the presence of glycidamide-DNA adducts as a marker for acrylamide exposure [18-20]. Glycidamide can react with glutathione (GSH), an important antioxidant within the body [21]. Prior studies have revealed that the varied toxic effects of acrylamide can be caused by genotoxic effects arising from oxidative DNA damage due to increased levels of intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and reduced GSH levels [22-25].
Within nervous tissues and the sciatic nerve, treatment with acrylamide causes increased lipid peroxidation and decreased antioxidant capacity [26]. In addition, acrylamide has been found to induce apoptosis in the cerebral cortex [27]. Some studies have suggested that acrylamide-induced cytotoxicity is influenced by oxidative stress [27-30], whereas some researchers have hypothesized that acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity occurs through axonal injury in the peripheral and central nervous system due to initial distal nerve terminal damage and a subsequent retrograde axon degeneration [31].
Grape seed has been shown to contain multiple hydroxyl groups; the pharmacological properties of which can play a therapeutic role against oxidative stress and oxygen free radicals [32]. Studies have suggested that grape seed can promote the production of Nitric Oxide (NO), an important signaling molecule involved in many physiological pathways [33]. Grape seed also contributes to the maintenance of healthy myocardial activity, and protects against insulin resistance induced by a high-fructose diet [34, 35]. Studies in human cancer cell lines have revealed that grape seed exerts effective anticancer effects against non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, neck and head squamous cancer, skin cancer, and cervical cancer [36-41]. Other studies using neonatal rat hypoxic-ischemic brain injury models have suggested that grape seed exhibits neuroprotective properties and suppresses free radical production after hypoxic ischemia injury, which may be a potential protective mechanism of grape seed extract [42].
In the present study, our aim was to investigate the effects of grape seed extract on the expression of selected antioxidant genes and the activity of antioxidant enzymes during acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in mice.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Acrylamide
Acrylamide was purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) with a purity of ≥ 99% (HPLC). In this study, 25 mg/kg body weight of acrylamide solution was freshly prepared by dissolving the powder in a saline solution.
2.2. Grape Seed
Grape seed was purchased from Korea Hanlim Co. (Hanlim Pharm. Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea). According to the manufacturer’s guidelines, the grape seed extract contained 89% proanthocyanidin, 6% monomers, and 5% other materials. In this study, 300 mg/kg of grape seed solution was freshly prepared by dissolving the powder in saline solution.
2.3. Animal Model and Treatment Design
Sixty adult Albino male mice (Mus musculus; average weight, 20–25 g) were bought from the animal house facility at King Fahd Center for Medical Research (King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia) in November 2018. The mice were kept in a room maintained under a controlled temperature of 25 ± 2°C and 12-h dark/light cycle. The mice had free access to food and water. After 1 week of acclimatization, the animals were divided into the following six groups (using a completely randomized design):
Group I: control, mice were orally administered saline solution once per day; Group II: mice were orally administered 25 mg/kg body weight acrylamide solution once per day for 20 days; Group III: mice were orally administered 25 mg/kg body weight acrylamide solution once per day for 10 days, and then 300 mg/kg body weight grape seed solution once per day for an additional 10 days; Group IV: mice were orally administered 300 mg/kg body weight of grape seed solution once per day for 10 days and then 25 mg/kg body weight of acrylamide solution once per day for an additional 10 days; Group V: mice were orally administered 25 mg/kg body weight acrylamide solution and 300 mg/kg body weight of grape seed solution once per day for 20 days; and Group VI: mice were orally administered 300 mg/kg body weight of grape seed solution once per day for 20 days. At the end of the trial period, the mice were euthanized, and their brain tissues were collected, rinsed with cold saline buffer, and stored at -80°C until needed for RNA isolation and biochemical assays.
2.4. Evaluation of Gene Expression
2.4.1. RNA Isolation
After the experiment, small sections of the brain were homogenized in 1 ml of TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Canada). Total RNA was isolated following the manufacturer’s instructions. The generated RNA was dissolved in diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), treated with water, and stored at -80°C until use. The yield and purity of the isolated RNA were evaluated using NanoDrop (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, California, USA).
2.4.2. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
From the isolated RNA, complementary DNA (cDNA) was produced following the manufacturer’s instructions using an Access RT-PCR System (Promega Corporation). The PCR mixture contained 1 mM antisense and sense primers (Table 1).
The following PCR conditions were used: reverse transcription of the first-strand cDNA, 1 cycle at 45°C for 45 min; AMV RT inactivation and RNA/cDNA/primer denaturation, 1 cycle at 94°C for 2 min; second-strand synthesis and PCR amplification, 40 cycles at 94°C for 30 s for denaturation, 60°C for 1 min for annealing, 68°C for 2 min for extension, and 1 cycle at 68°C for 7 min for final extension.
2.5. Biochemical Assays
2.5.1. Preparation of Tissue Homogenates for Biochemical Assays
Brain tissues were separately homogenized at a concentration of 25 mg/ml using ice-cold homogenizing medium (0.1 M sodium phosphate with 5 mM EDTA buffer, pH 8). Homogenates were centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 20 min. Subsequently, the supernatants were transferred to new tubes for immediate assaying to derive total protein content using biochemical assay kits, or were stored at -80°C until use [43].
2.5.2. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation (LPO) Activities
LPO activities were assessed using Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA) with a purity of ≥ 99% (BDH, England), as described previously [44]. Briefly, 100 µl of brain tissue homogenate was mixed with 1.5 ml of 0.8% TBA, 1.5 ml of 20% glacial acetic acid, 200 µl of 8.1% SDS, and 600 µl distilled water. The mixture was then vortexed and heated for 1 h at 95°C in a water bath. The tubes were subsequently cooled to 25°C and centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 20°C. The absorbance of each tube was measured using a UV-visible spectrophotometer at 532 nm. All the concentrations are reported as nmol.
2.5.3. Measurement of Reduced Glutathione (GSH) Activities
To evaluate the levels of reduced GSH in the brain, a previously described method was used [45]. Briefly, 200 µl of the homogenate of each tissue was mixed with 400 µl of lysis buffer (10 mM Tris, 0.2% triton, and 1 mM EDTA), incubated on ice for 30 min, and centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 20 °C. Two hundred µl of the supernatant was transferred to a new tube and mixed with 400 µl of 0.1 M sodium phosphate pH 8.0 containing 1 mM EDTA and 100 µl of 10 µM 5,5-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB; Ellman's Reagent). The absorbance of each tube was measured using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (model PharmaSpec 1700, Shimadzu, Japan), at 412 nm, and compared to that of a blank reagent. To determine the GSH levels in mmol/g of the sample, the absorbance values of the samples were compared to those of a standard curve produced using the known concentrations of GSH.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
GraphPad Prism version 6.04 (La Jolla, California, USA) and SPSS 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA) were used for statistical analysis. The differences between groups were evaluated using a one-way analysis of variance (nonparametric), followed by post-hoc Duncan’s test. Data are expressed as mean ± Standard Deviation (SD). P < 0.05 (two-sided P-values) was considered to indicate significance.
3. RESULTS
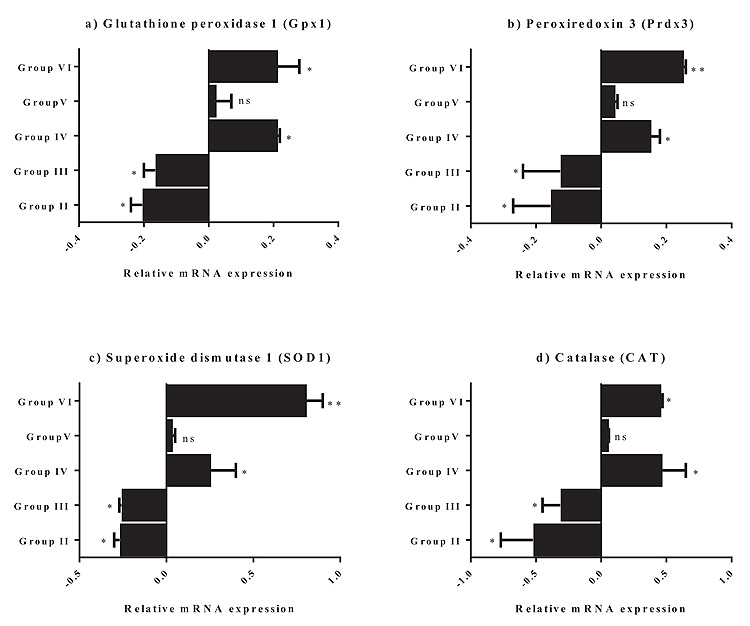
3.1. Potential Effect of Grape Seed Extract on the Expression of Antioxidant Genes
The effect of grape seed treatment alone, before, after, or in combination with acrylamide on Gpx1, Prdx3, SOD1, and CAT gene expression levels in mouse brain tissues was investigated (Fig. 1). Animals treated with acrylamide only (Group II) showed a significant decrease in the expression levels of Gpx1 (P < 0.05), Prdx3 (P < 0.05), SOD1 (0.05), and CAT (P < 0.05), relative to those of the untreated controls (Group I). Treatment with grape seed after exposure to acrylamide (Group III) did not have any neuroprotective effect against acrylamide-induced cytotoxicity, as shown by significant decreases in the expression levels of Gpx1 (P < 0.05), Prdx3 (P < 0.05), SOD1 (P < 0.05), and CAT (P < 0.05), relative to those in the untreated controls (Group I).
Treatment with grape seed before exposure to acrylamide (Group IV), or together with acrylamide (Group V), exhibited a protective effect against acrylamide toxicity, restoring the expression levels of Gpx1, Prdx3, SOD1, and CAT to values similar to those in the control group (Group I) or more, as seen in Group IV (P < 0.05). Animals treated with grape seed only (Group VI) showed a significant increase in the expression levels of Gpx1 (P < 0.05), Prdx3 (P < 0. 01), SOD1 (P < 0.01), and CAT (P < 0.05), compared to those in the untreated controls (Group I).
| No. | Primer | Sequence 5′–3′ | Tm | Length | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gpx1_forward | ATTGCCTCCAAATACAACCTC | 50.3 °C | 21bp | 408bp |
| Gpx1_reverse | TGCGTCATCAAAAGGCTTC | 50.9 °C | 19bp | ||
| 2 | Prdx3_forward | AGTATTTCTGCCTCAACAGTTC | 50.5 °C | 22bp | 399bp |
| Prdx3_reverse | GCCCAAACCACCATTCTTTC | 51.8 °C | 20bp | ||
| 3 | SOD 1_forward | ACTTCGAGCAGAAGGCAAG | 52.1 °C | 19bp | 458bp |
| SOD 1_reverse | GCAATCCCAATCACTCCAC | 50.6 °C | 19bp | ||
| 4 | CAT_forward | ACAACACACATACCACACAC | 50.5 °C | 20bp | 392bp |
| CAT_reverse | GCTGAAAGCAACCAAACAC | 50.3 °C | 19bp | ||
| 5 | GAPDH_forward | CCCCTTCATTGACCTCAACTAC | 52.5 °C | 22bp | 420bp |
| GAPDH_reverse | ATGAGCCCTTCCACAATGC | 52.3 °C | 19bp |
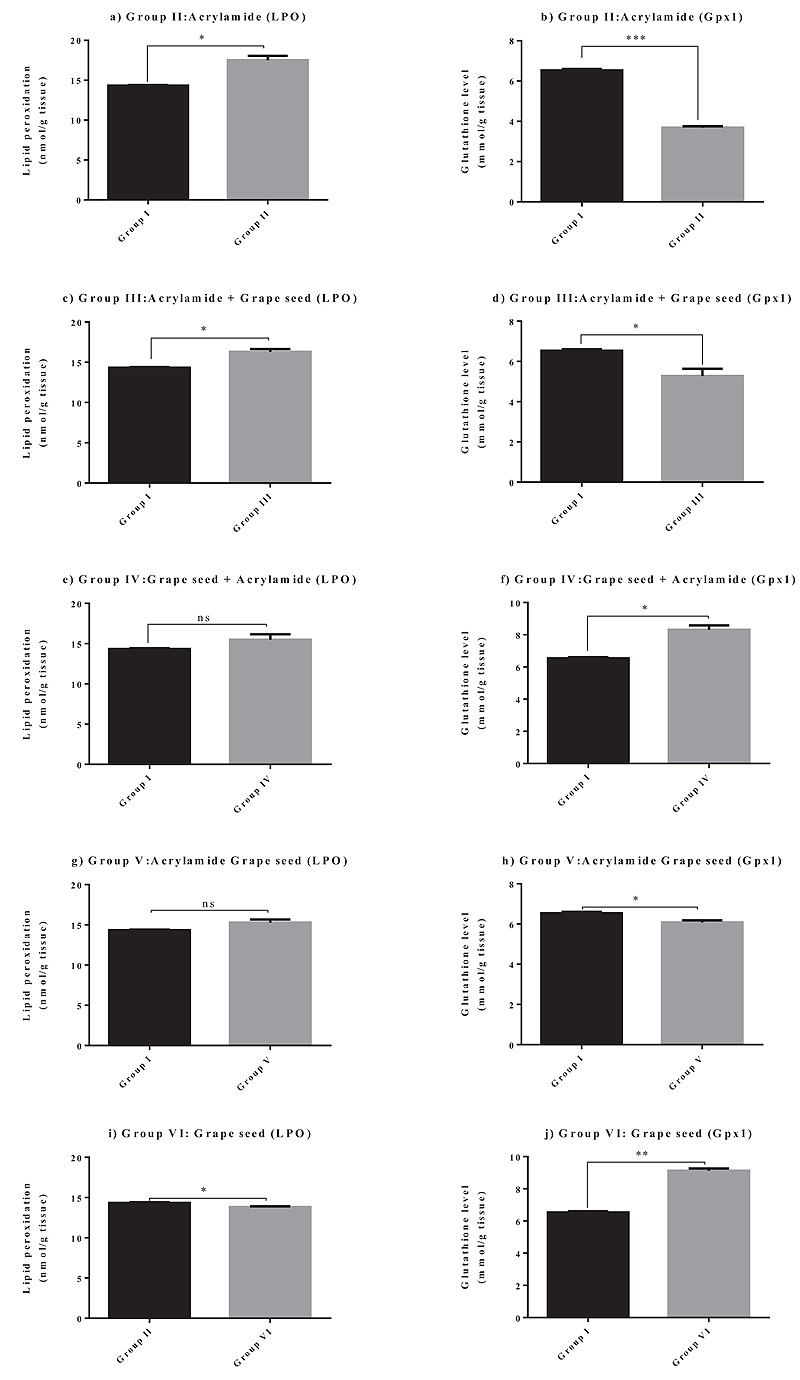
3.2. Effect of Grape Seed on GSH Levels and LPO Activities
The effect of grape seed treatment alone, before, after, or in combination with acrylamide on GSH levels and LPO activities in mouse brain tissues was determined (Table 2). Animals treated with acrylamide alone (Group II) showed a marked increase in the LPO activities (P < 0.05) and a significant decrease in the GSH levels (P < 0.05) in brain tissues, compared to those in the untreated controls (Group I). Animals treated with grape seed after acrylamide treatment (Group III) showed an evident increase in the LPO activities (P < 0.05) and a significant decrease in the GSH levels (P < 0.05) in brain tissues, relative to those in the untreated controls (Group I). Animals treated with grape seed before acrylamide treatment (Group IV) showed no significant change in the LPO
| Treatment | Lipid Peroxidation (nmol/g tissue) |
Glutathione Level (mmol/g tissue) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 14.264 ± 0.410 b | 6.483 ± 0.123 b |
| Grape seed | 13.782 ± 0.054 c | 9.024 ± 0.115 a |
| Acrylamide | 17.121 ± 0.522 a | 3.634 ± 0.152 c |
| Grape seed + Acrylamide | 15.953 ± 0.842 b | 8.102 ± 0.163 a |
| Acrylamide + Grape seed | 16.035 ± 0.104 a | 5.530 ± 0.041 cb |
| Acrylamide Grape seed | 15.541 ± 0.178 b | 4.230 ± 0.346 c |
activities compared to those in the untreated controls (Group I) and a significant increase in the GSH levels in brain tissues, relative to those in the untreated controls (Group I). Animals treated with grape seed and acrylamide simultaneously (Group V) showed no significant change in the LPO and GSH activities, compared to those in the untreated controls (Group I). The LPO activities (P < 0.05) evidently decreased, whereas the GSH (P < 0.05) levels significantly increased in the brain tissues of animals treated with grape seed alone (Group VI), compared to those in the untreated controls (Group I). The GSH levels for Group IV seemed to be significantly increased as compared to those for Group I.
It can be concluded from these results that the best treatment that helped achieve more antioxidant effect was when the animals were treated with grape seed before exposure to acrylamide (Group IV), and they also exhibited a protective effect against acrylamide toxicity; this effect seems to be considerably similar to that observed for Group V.
4. DISCUSSION
The results of the present study confirmed that acrylamide increased oxidative stress in brain tissues by downregulating the expression of specific antioxidant genes, including CAT, Gpx1, SOD1, and Prdx3; such downregulation occurred because of an elevation in the LPO activities and reduction in the GSH levels.
LPO activity, which is expressed as a thiobarbituric acid reactive substance, is an important measure of oxidative stress. Studies have shown that an increase in the LPO activity is associated with a significant decrease in the levels of GSH, which is an important antioxidant defense mechanism. The results found in this study agree with those of the previous studies, where treatment with acrylamide increased the LPO activity levels and decreased the GSH levels in the cerebral cortex [31, 46].
The action of acrylamide is typical among many chemical toxicants that can cause central-peripheral distal axonopathy [47]. Acrylamide may initially target the nerve terminals in both the peripheral and central nervous system, ultimately causing motor, autonomic, sensory, and behavioral disturbances [48-53] (Fig. 2).
Studies have indicated that acrylamide depletes GSH content and inhibits glutathione S-transferase activity [54]. Acrylamide also reacts with important cellular nucleophiles that contain –SH, –OH, or –NH2. Hence, acrylamide interacts with GSH in a similar manner to form GSH S-conjugates, which is the first step for the biotransformation of electrophiles into mercapturic acid [55]. These changes lead to an imbalance in the oxidant/antioxidant levels, which initiate cellular damage induced by oxidative stress. Studies have also shown that GSH conjugation is an important detoxification mechanism for acrylamide toxicity [55-57].
Studies have suggested that oxidative stress plays an important role in acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity, and that antioxidants can effectively alleviate acrylamide toxicity. For example, Acorus calamus [58], thymoquinone [59], and crocin [60, 61] are powerful antioxidant agents that exhibit neuroprotective effects in models of acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity.
Grape seed has a high content of polyphenols [62], which have been shown to possess antioxidant properties [63-65]. Studies have suggested that grape seed is an effective and safe antioxidant compound [66, 67]. It acts as a potent antioxidant and has exhibited neuroprotective properties, even in damaged neurons [68]. Neuropharmacological studies based on animal and cellular models have also shown that treatment with resveratrol has significant beneficial effects on memory and cognitive function [69-75].
The effect of grape seed on the cytotoxicity induced by acrylamide in a mouse model was evaluated in the present study. Exposure to acrylamide was found to significantly reduce the expression of the studied antioxidant genes and the activity of the corresponding enzymes. Treatment with grape seed extract before or during acrylamide exposure helped to restore antioxidant parameters in the animals to normal levels. However, treatment with grape seed after exposure to acrylamide led to no related increase in the antioxidant gene expression and enzyme activity in the mice. Therefore, we concluded that grape seed was only protective before or during exposure to acrylamide, and that these effects may be attributed to the potent antioxidant properties of the extract.
When comparing the antioxidant activity of grape seeds with the effect of other antioxidants known to protect against acrylamide toxicity, such as linalool or curcumin, the results showed that grape seeds have a similar effect as mentioned in these studies; however, the present study showed more evidence at the molecular level and with low doses (25 mg/kg) of acrylamide and with longer time when compared to other studies (20 days). Regarding the antioxidant activity of linalool, research has shown that 100 mg linalool could increase the level of glutathione and decrease the level of lipid peroxidation protein after treatment with or before exposure to 50 mg/kg of acrylamide, in approximately 3 days [76].
Another group of researchers found that rats that had their diet supplemented with turmeric (0.5%) and 340 mg/kg of acrylamide simultaneously for 11 days, showed improved antioxidant levels in the brain tissue and a protective effect against acrylamide toxicity [77].
The limitations of the present study include the small sample size, our inability to extrapolate these results to humans at present, and our inability to ascertain concrete molecular, biochemical, and cellular mechanisms of the effects evaluated. Moreover, an important limitation of our study is that we could not analyze the effect of grape seed extracts on neurotoxicity using immunohistological analysis with neurotoxicity markers and apoptotic markers, which would have been more useful in the validation of our findings.
CONCLUSION
In summary, this study revealed that grape seed extract reduced acrylamide-induced toxicity in mouse models, and that this effect of grape seed extract could be due, in part, to its significant antioxidant properties. However, further studies are needed to clarify the exact mechanism of its neuroprotective effects and to elucidate the molecular and cellular mechanisms of these effects.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
This protocol was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of Taif University, Taif, KSA (1-439-6093).
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
No humans were used in the study. This study was carried out in accordance with the NC3Rs ARRIVE Guidelines for in vivo Experiments. The procedures followed for handling and treating mice were in accordance with the standards set forth in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals [78].
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
The data supporting the findings of the article is available within the article.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author declares no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author is thankful to her colleagues in the Biotechnology Department at Taif University for their support.


